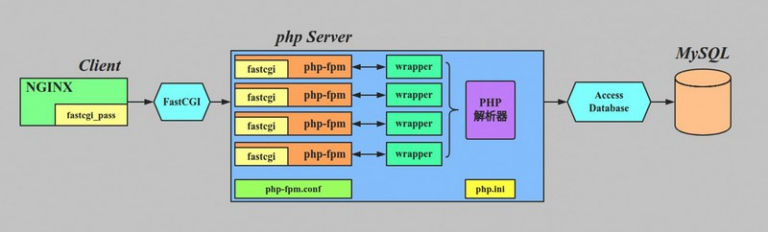
Below is a focused, production-oriented checklist of important topics to learn in MySQL, organized from fundamentals → advanced → operations. This is the skill set expected of backend engineers working with real MySQL systems.
Important Topics to Learn in MySQL
1. MySQL Fundamentals
- MySQL architecture (client → server → storage engine)
- Databases, tables, rows, columns
- Character sets & collations (utf8mb4 vs utf8)
- Data types (INT, BIGINT, VARCHAR, TEXT, DATE, TIMESTAMP, JSON)
- NULL behavior and defaults
2. SQL Basics (Daily Usage)
SELECT,INSERT,UPDATE,DELETEWHERE,ORDER BY,LIMIT,OFFSETDISTINCTCASEexpressions
3. Filtering & Aggregation
AND,OR,IN,BETWEEN,LIKECOUNT,SUM,AVG,MIN,MAXGROUP BYHAVING
4. Joins & Relationships (Critical)
INNER JOINLEFT JOIN,RIGHT JOIN- Self joins
- Many-to-many relationships
- Join order & performance impact
Most performance problems start with bad joins.
5. Indexing (Very Important)
- B-Tree indexes (default)
- Primary vs secondary indexes
- Composite (multi-column) indexes
- Covering indexes
- Index selectivity
- When NOT to add an index
6. Storage Engines (Must Know)
InnoDB (Default)
- Clustered index
- Row-level locking
- MVCC
- Redo / undo logs
MyISAM (Legacy)
- Table-level locking
- Why it’s mostly avoided
7. Constraints & Data Integrity
PRIMARY KEYFOREIGN KEYUNIQUENOT NULLCHECK(MySQL 8+)- Cascading rules (
ON DELETE,ON UPDATE)
8. Transactions & ACID
START TRANSACTION,COMMIT,ROLLBACK- Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability
- Autocommit behavior
- Savepoints
9. Isolation Levels & Locking
- Read Uncommitted
- Read Committed
- Repeatable Read (default in MySQL)
- Serializable
- Gap locks
- Deadlocks & detection
10. Query Optimization
EXPLAINEXPLAIN ANALYZE- Query execution order
- Index usage analysis
- Avoiding full table scans
This is where senior-level MySQL skill starts.
11. Schema Design & Normalization
- 1NF, 2NF, 3NF
- When to denormalize
- OLTP-friendly schema design
- Avoiding over-indexing
12. Advanced SQL
- Subqueries (correlated & non-correlated)
- Common Table Expressions (CTEs – MySQL 8+)
- Window functions (
ROW_NUMBER,RANK) - JSON functions (
JSON_EXTRACT,JSON_CONTAINS)
13. Stored Logic
- Stored procedures
- Functions
- Triggers
- Events (MySQL Scheduler)
- Pros & cons in application design
14. Security & Access Control
- Users & roles
GRANT/REVOKE- Host-based access
- Password authentication plugins
- SQL injection prevention
15. Backup & Recovery (Production-Critical)
- Logical backups (
mysqldump) - Physical backups
- Restore strategies
- Backup verification
- Point-in-time recovery basics
16. Replication & High Availability
- Primary-Replica replication
- Binary logs (binlog)
- Replication lag
- Read replicas
- Failover basics
17. Partitioning & Scaling
- Range, Hash, List partitioning
- Vertical vs horizontal scaling
- Read scaling strategies
- Connection pooling concepts
18. Performance & Monitoring
- Slow query log
- Performance Schema
- Information Schema
- Index statistics
- Disk I/O bottlenecks
19. MySQL Configuration & Tuning
innodb_buffer_pool_sizemax_connectionsquery_cache(deprecated)- Thread handling
- Memory vs disk tradeoffs
20. MySQL + Application Integration
- ORM behavior (Django, Laravel, SQLAlchemy)
- N+1 query problem
- Transactions in app code
- Migration strategies
Learning Priority (If You’re Time-Constrained)
Phase 1 – Must Know
- SQL basics
- Joins
- Indexing
- Transactions
- InnoDB fundamentals
Phase 2 – Professional Level
- Query optimization
- Isolation levels
- Replication basics
- Schema design
Phase 3 – Production / Senior
- Backups & recovery
- Scaling & partitioning
- Monitoring & tuning
- High availability