FastCGI for PHP Explained: What It Is, How It Works, and Why You Should Use It
Modern PHP applications demand speed, scalability, and security. This is where FastCGI for PHP comes in. If you are running WordPress, WooCommerce, Laravel, or any production PHP application, FastCGI is no longer optional—it’s the standard.
In this guide, we’ll explain what FastCGI is, which web servers support it, and why FastCGI + PHP-FPM is the best way to run PHP today.
What Is FastCGI for PHP?
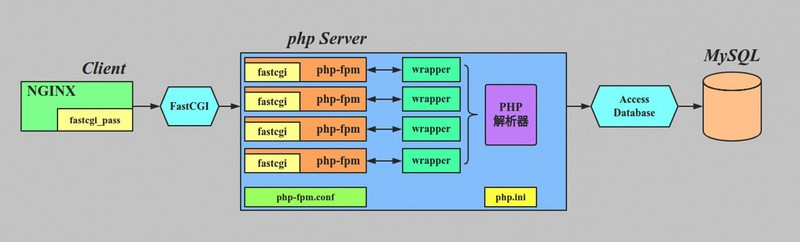
FastCGI is a protocol that allows a web server to communicate with an external application process—in this case, PHP—using persistent connections.
Instead of starting a new PHP process for every request (as traditional CGI does), FastCGI keeps PHP processes alive and reuses them.
In real-world PHP setups, FastCGI is almost always implemented using PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager).
Typical Architecture
Browser → Web Server → FastCGI → PHP-FPM → PHP
How PHP Execution Has Evolved
CGI (Legacy – Not Recommended)
- Starts a new PHP process per request
- Very slow and resource-heavy
- Poor scalability
mod_php (Apache Only – Legacy)
- PHP runs inside Apache
- High memory usage
- Poor isolation and flexibility
FastCGI + PHP-FPM (Modern Standard)
- PHP runs as a separate, persistent service
- Excellent performance and scalability
- Strong process isolation
✅ This is the architecture used in modern production environments
What Is PHP-FPM?
PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) is a PHP service that:
- Maintains a pool of PHP worker processes
- Handles concurrent requests efficiently
- Controls memory usage, execution limits, and timeouts
- Supports multiple PHP versions and users on the same server
Think of PHP-FPM as a PHP application server, similar to how Gunicorn works for Python or Puma for Ruby.
Web Servers That Support FastCGI for PHP
Nginx
- Native FastCGI support
- No built-in PHP engine
- Requires PHP-FPM
- Extremely fast and resource-efficient
Best choice for high-traffic WordPress and APIs
Apache HTTP Server
- Uses
mod_proxy_fcgi - Can fully replace
mod_php - Works well with PHP-FPM
Recommended modern Apache setup
LiteSpeed
- FastCGI compatible
- Optimized for PHP workloads
- Common in managed WordPress hosting
Microsoft IIS
- Supports FastCGI via IIS modules
- Mostly used on Windows servers
Why You Should Use FastCGI for PHP
1. Better Performance
- PHP processes are reused
- No fork-per-request overhead
- Faster response times under load
📈 Result: Faster websites and APIs
2. Superior Scalability
PHP-FPM allows fine-grained tuning:
pm.max_childrenpm.start_serverspm.max_requests
This ensures predictable performance during traffic spikes.
📈 Result: Stable behavior under high traffic
3. Improved Security
- PHP runs outside the web server
- Separate users per site or pool
- Reduced attack surface
🔐 Result: Better isolation and security
4. Efficient Resource Utilization
- Web server handles static files and TLS
- PHP-FPM handles PHP only
- Lower memory footprint
⚙️ Result: More traffic with the same server
5. DevOps & Cloud Friendly
- Works perfectly with Docker and Kubernetes
- Supports zero-downtime reloads
- Easy multi-PHP-version setups
☁️ Result: Production-ready architecture
Example: FastCGI Configuration in Nginx
location ~ \.php$ {
include snippets/fastcgi-php.conf;
fastcgi_pass unix:/run/php/php8.1-fpm.sock;
}
Request Flow
- Browser requests a
.phpfile - Nginx forwards it via FastCGI
- PHP-FPM executes PHP
- Output is returned to Nginx
- Nginx sends response to the browser
When Should You Avoid FastCGI?
FastCGI may be unnecessary if:
- You are running a very small local development setup
- You are on legacy shared hosting with no PHP-FPM access
For any production environment, FastCGI is strongly recommended.
FastCGI vs Other PHP Execution Models (Summary)
| Feature | FastCGI + PHP-FPM |
|---|---|
| Performance | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Scalability | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Security | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Resource Control | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Production Ready | ✅ |
Final Thoughts
If you are running:
- WordPress or WooCommerce
- Laravel or Symfony
- Any modern PHP application
👉 FastCGI with PHP-FPM is the correct and future-proof choice
It delivers better performance, stronger security, and easier scaling compared to legacy PHP execution models.